OpenAI will cut off API access for Chinese developers on July 9. This decision affects all OpenAI platforms, including GPT-3 and DALL-E. It follows earlier restrictions on consumer-facing applications like ChatGPT in China.
The move impacts Chinese developers who have been using these tools for various applications. It represents a significant shift in OpenAI’s global accessibility strategy.
API Access: More Critical Than Consumer Apps

The API is considered more crucial than consumer-facing applications. Developers use the API to power apps for form-filling, data analysis, and automation. Chinese developers currently have access to these tools but only for a short time.
The loss of API access will have a more profound impact on Chinese AI development. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global AI market size is expected to grow from $58.3 billion in 2021 to $309.6 billion by 2026.
Chinese Competitors Seize Market Opportunity

Chinese AI companies like Zhipu AI are capitalizing on this situation. They are actively trying to attract developers to their platforms. Most apps can reportedly transfer from one AI model to another relatively easily.
However, Chinese platforms face significant hardware limitations due to U.S. restrictions. The global AI chip market, dominated by NVIDIA, is projected to reach $83.25 billion by 2027, according to Fortune Business Insights.
U.S. Government Policy Drives Restrictions

The U.S. government’s policies have largely influenced these restrictions. Many U.S. tech industry leaders support these measures. AI models are increasingly treated as a national security issue.
This approach reflects a shift in how consumer technology is viewed in geopolitical contexts. The U.S. government has implemented various export controls on AI technologies, including restrictions on high-end AI chips to China in 2022.
Rise of Hawkish CEOs in Tech

A new generation of tech CEOs views great power conflict as inevitable. They see AI as a critical component of this conflict. This perspective influences their business strategies and public statements.
Scale AI CEO Alexandr Wang exemplifies this hawkish stance. According to a CSET survey, 61% of AI researchers believe AI will have a large impact on national security by 2040.
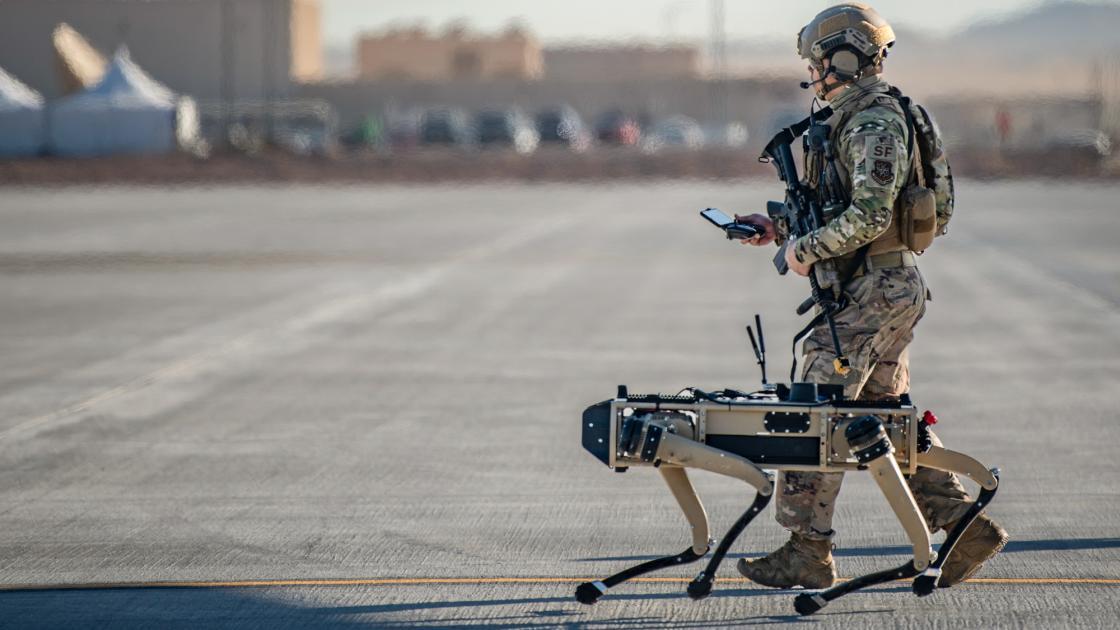
AI as a Military Technology
Many industry leaders view AI as a crucial military technology. They argue that the U.S. government must lead in AI development. This perspective drives both private sector innovation and government funding.
The U.S. Department of Defense has increased its AI budget significantly. In fiscal year 2023, the DoD requested $1.56 billion for AI-related projects, a 50% increase from the previous year.
Financial Incentives Shape AI Narratives

Companies like Scale AI benefit financially from military contracts. Scale AI is completing a $100 million contract with the DoD. This financial relationship influences public discourse on AI’s military potential.
It creates a feedback loop between industry narratives and government spending. The U.S. government’s investment in AI for defense purposes is expected to reach $1.8 billion annually by 2025, according to Govini.
OpenAI’s Role in Shaping AI Discourse

OpenAI has consistently promoted the strategic importance of AI. This stance has become standard for U.S. companies in the AI sector. OpenAI’s influence extends beyond its technical innovations.
Its public statements shape policy discussions and industry norms. According to a Stanford University report, mentions of AI in U.S. Congressional records increased by 285% between 2016 and 2020.
U.S.-China Tech Sector Divide Deepens

The AI industry is witnessing a growing divide between U.S. and Chinese sectors. This separation creates new market opportunities for U.S. companies. It also raises concerns about global technological fragmentation.
The long-term implications of this divide remain uncertain. A Brookings Institution report suggests that this tech decoupling could cost the global economy up to $3.5 trillion by 2025.
Questioning AI’s Military Value

Some experts question the assumed military value of AI models. AI has proven useful in software development and pharmaceutical research. However, its impact on warfare remains speculative.
The uncertainty surrounding AI’s military applications raises concerns about large investments. A RAND Corporation study found that while AI has potential military applications, its battlefield effectiveness remains largely unproven.

